Nanoparticles made from corn juice inhibit tumor growth in mice
Date: 14.2.2022
With the ability to be finely engineered to tackle the disease in different ways, nanoparticles hold huge potential when it comes to cancer treatment. Researchers at the Tokyo University of Science have now demonstrated a low-cost and highly promising form of this technology, using corn and water as a starting point for a novel "bionanoparticle" that suppresses tumor growth in mice.
 We've seen nanoparticles developed to take the fight to cancer in many ways, from light-activated versions that rob cancerous cells of essential proteins, to versions that detect and track tumors months ahead of traditional imaging techniques, to name just a couple of examples.
We've seen nanoparticles developed to take the fight to cancer in many ways, from light-activated versions that rob cancerous cells of essential proteins, to versions that detect and track tumors months ahead of traditional imaging techniques, to name just a couple of examples.
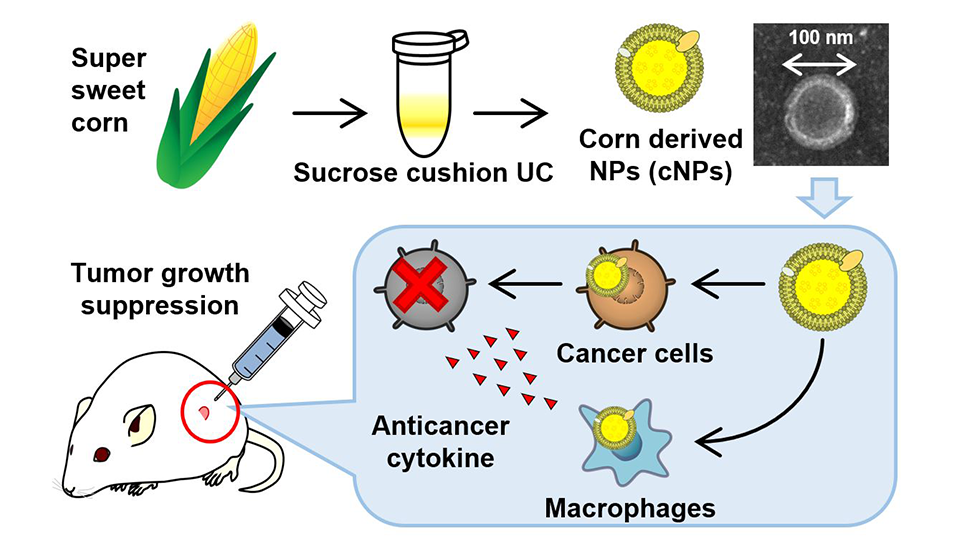
But these synthetic particles, which measure between one and 100 nanometers in size, are difficult and expensive to produce, leading the authors of this new study to investigate another possibility in the form of plant-derived nanoparticles.
The experiments involved creating a mixture of super sweet corn and water, with this corn juice then centrifuged at high speed and filtered through a syringe with an opening of 0.45 ?m. These filtered samples where then ultracentrifuged, allowing the team to extract tiny corn-derived nanoparticles around 80 nanometers in diameter.
In testing out their new nanoparticles, the scientists found that they were taken up by a range of cells, including tumor cells derived from mice, and macrophage-like cells called RAW264.7. Describing the results as astounding, the team watched as their nanoparticles triggered an immune response and released a tumor-killing factor from the RAW264.7 cells. They also showed a high selectivity for the tumor cells, and ultimately, significantly inhibited their growth.
-























