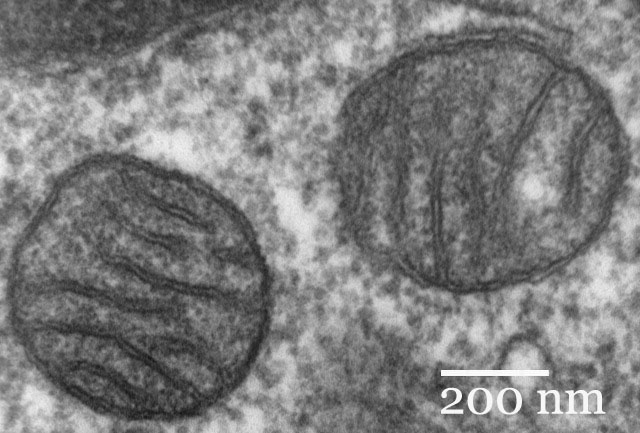
mitochondrion

In cell biology, a mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells.
These organelles range from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometer (μm) in diameter. Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.
In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in a range of other processes, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, cell death, as well as the control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders and cardiac dysfunction, and may play a role in the aging process.
The number of mitochondria in a cell varies widely by organism and tissue type. Many cells have only a single mitochondrion, whereas others can contain several thousand mitochondria.
The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix.