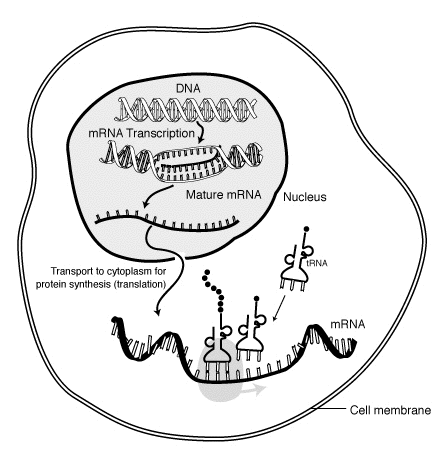
mRNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a molecule of RNA that encodes a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomes. Here, the nucleic acid polymer is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein.
In mRNA as in DNA, genetic information is encoded in the sequence of nucleotides arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA) mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, whereas ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.