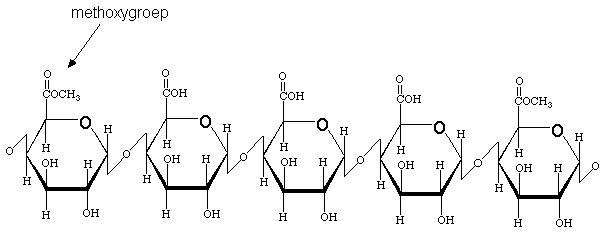
pectin

Pectin is a structural heteropolysaccharide contained in the primary cell walls of terrestrial plants.
It was first isolated and described in 1825 by Henri Braconnot.
In plant cells, pectin consists of a complex set of polysaccharides that are present in most primary cell walls and are particularly abundant in the non-woody parts of terrestrial plants. Pectin is present not only throughout primary cell walls but also in the middle lamella between plant cells, where it helps to bind cells together.
Pectin is a natural part of the human diet, but does not contribute significantly to nutrition. The daily intake of pectin from fruits and vegetables can be estimated to be around 5 g (assuming consumption of approximately 500 g fruits and vegetables per day).
In human digestion, pectin binds to cholesterol in the gastrointestinal tract and slows glucose absorption by trapping carbohydrates. Pectin is thus a soluble dietary fiber.
It is produced commercially as a white to light brown powder, mainly extracted from citrus fruits, and is used in food as a gelling agent particularly in jams and jellies. It is also used in fillings, medicines, sweets, as a stabilizer in fruit juices and milk drinks, and as a source of dietary fiber.