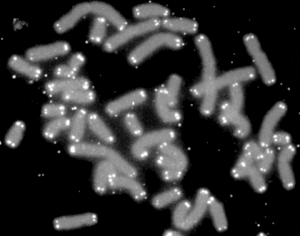
telomeres

A telomere is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences at each end of a chromosome, which protects the end of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes.
Telomere regions deter the degradation of genes near the ends of chromosomes by allowing chromosome ends to shorten, which necessarily occurs during chromosome replication. Over time, due to each cell division, the telomere ends become shorter.
During cell division, enzymes that duplicate DNA cannot continue their duplication all the way to the end of chromosomes. If cells divided without telomeres, they would lose the ends of their chromosomes, and the necessary information they contain. The telomeres are disposable buffers blocking the ends of the chromosomes, are consumed during cell division, and are replenished by an enzyme, telomerase reverse transcriptase.