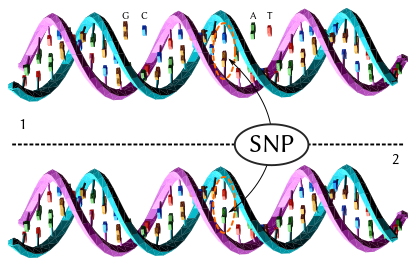
single-nucleotide polymorphism

A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide in the genome differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes in an individual.
Almost all common SNPs have only two alleles. The genomic distribution of SNPs is not homogenous, SNPs usually occur in non-coding regions more frequently than in coding regions or, in general, where natural selection is acting and fixating the allele of the SNP that constitutes the most favorable genetic adaptation.
These genetic variations between individuals are exploited in DNA fingerprinting, which is used in forensic science. Also, these genetic variations underlie differences in our susceptibility to, or protection from all kinds of diseases.