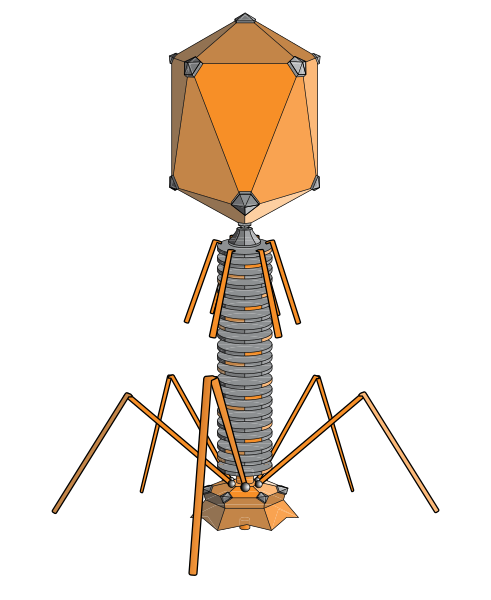
bacteriophage

A bacteriophage is any one of a number of viruses that infect bacteria. They do this by injecting genetic material, which they carry enclosed in an outer protein capsid.
The genetic material can be ssRNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, or dsDNA ('ss-' or 'ds-' prefix denotes single-strand or double-strand) along with either circular or linear arrangement.
Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. The term is commonly used in its shortened form, phage.
Phages are widely distributed in locations populated by bacterial hosts, such as soil or the intestines of animals. One of the densest natural sources for phages and other viruses is sea water.
They are seen as a possible therapy against multi-drug-resistant strains of many bacteria.