protein biosynthesis

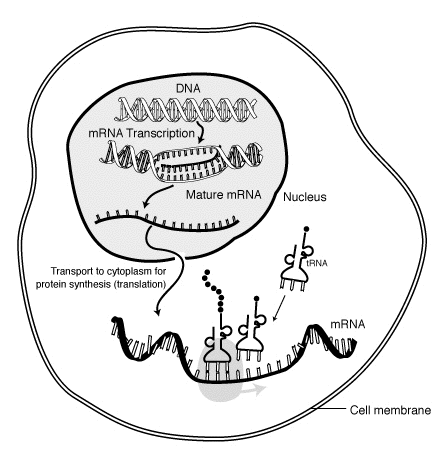
Protein biosynthesis is the process in which cells build or manufacture proteins. The term refers to a multi-step process, beginning with amino acid synthesis and transcription of nuclear DNA into messenger RNA, which is then used as input for translation.
In protein synthesis, a succession of tRNA molecules charged with appropriate amino acids are brought together with an mRNA molecule and matched up by base-pairing through the anti-codons of the tRNA with successive codons of the mRNA. The amino acids are then linked together to extend the growing protein chain, and the tRNAs, no longer carrying amino acids, are released. This whole complex of processes is carried out by the ribosome, formed of two main chains of RNA, called ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and more than 50 different proteins. The ribosome latches onto the end of an mRNA molecule and moves along it, capturing loaded tRNA molecules and joining together their amino acids to form a new protein chain.