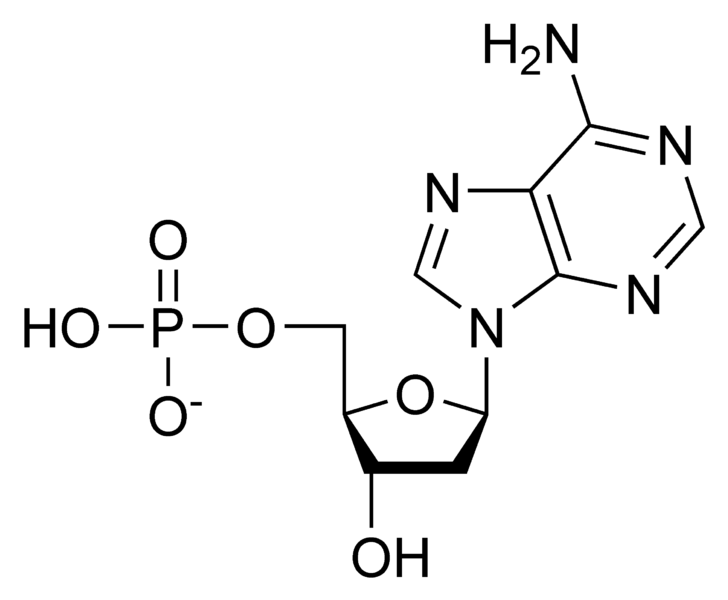
deoxyribonucleotide

A deoxyribonucleotide is the monomer, or single unit, of DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and one phosphate group. The nitrogenous base is always bonded to the 1st carbon of the deoxyribose, which is distinguished from ribose by the presence of a proton on the 2nd carbon rather than an -OH group. The phosphate groups bind to the 5th carbon of the sugar.
When deoxyribonucleotides polymerize to form DNA, the phosphate group from one nucleotide will bond to the 3rd carbon on another nucleotide, forming a phosphodiester bond via dehydration synthesis. New nucleotides are always added to the 3rd carbon of the last nucleotide, so synthesis always proceeds from 5th to 3rd.