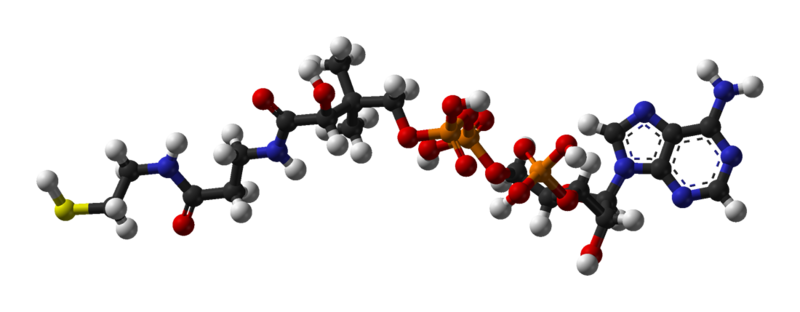
coenzyme A

Coenzyme A (CoA, CoASH, or HSCoA) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle.
All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester, such as acetyl-CoA) as a substrate.
It is adapted from cysteamine, pantothenate, and adenosine triphosphate.